https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/49189
프로그래머스
코드 중심의 개발자 채용. 스택 기반의 포지션 매칭. 프로그래머스의 개발자 맞춤형 프로필을 등록하고, 나와 기술 궁합이 잘 맞는 기업들을 매칭 받으세요.
programmers.co.kr
1. 이차원 배열로 그래프 구현
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Solution {
static boolean[][] graph;
static int n;
static Queue<Integer> queue;
static boolean[] visited;
public int solution(int n, int[][] edge) {
int answer = 0;
graph = new boolean[n+1][n+1];
for(int i=0;i<edge.length;i++){
int x = edge[i][0];
int y = edge[i][1];
graph[x][y] = true;
graph[y][x] = true;
}
queue = new LinkedList<>();
visited = new boolean[n+1];
queue.add(1);
visited[1] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
int tmp = queue.poll();
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
if(graph[tmp][j] && !visited[j]){
queue.add(j);
visited[j] = true;
}
}
}
answer= size;
}
return answer;
}
}
2. 연결리스트로 그래프 구현
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Solution {
static int n;
static Queue<Integer> queue;
static boolean[] visited;
public int solution(int n, int[][] edge) {
int answer = 0;
//그래프 구현
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> list=new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
for(int i=0;i<edge.length;i++){
list.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
//노드 연결
int a, b;
for(int[] node:edge){
a=node[0];
b=node[1];
list.get(a).add(b);
list.get(b).add(a);
}
queue = new LinkedList<>();
visited = new boolean[n+1];
queue.add(1);
visited[1] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
int tmp = queue.poll();
for(int v:list.get(tmp)){
if(!visited[v]){
visited[v]=true;
queue.add(v);
}
}
}
answer = size;
}
return answer;
}
}
노드 간 최단 거리를 구할 수 있는 bfs를 활용한다.
가장 멀리 떨어져있는 노드의 개수는 가장 마지막 큐 사이즈이다.
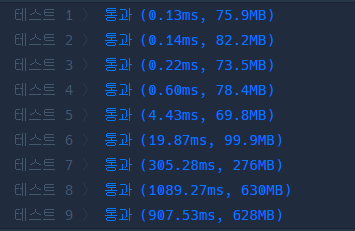
그래프를 이차원 배열로 구현하느냐 연결리스트로 구현하느냐에서 속도 차이가 많이 나는 것을 알 수 있다. 웬만하면 연결리스트로 하는게 좋을 것 같다.
'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [PGS] 프로그래머스 - 다리를 지나는 트럭 (JAVA) (0) | 2023.03.08 |
|---|---|
| [PGS] 프로그래머스 - 단어 변환 (JAVA) (0) | 2023.02.28 |
| [PGS] 프로그래머스 - 체육복 (JAVA) (0) | 2023.02.22 |
| [BOJ] 6603번: 로또 (JAVA) (0) | 2023.02.20 |
| [PGS] 프로그래머스 - 소수찾기 (JAVA) (0) | 2023.02.16 |